For design engineers in the process of selecting components for an application, the motor or gearmotor can be one of the more difficult components to source. There are so many types of motors and gearmotors all screaming for your attention and promising to be the “most efficient”, the “highest quality” or boasting about “high precision”. Groschopp uses 4 simple steps to lead designers to the best motor/gearmotor choice for a particular application. There are several key design parameters that should be considered when selecting a motor or gearmotor for a motion control application.
Table 1:gear reduction stepper motorSelection Process – steps to complete to ensure a gearmotor properly matches the application

Table 2: Application Checklist – use this checklist to help formulate the specific requirements to ensure the gearmotor vendor has the critical information necessary to achieve the best match between the gearmotor and the application:

Table 3: Motors Quick Reference Guide – provides a comparison of common parameters used during the motor selection process;

As the designer looks at selecting a gearmotor, there are two methods that can be used.
Method 1: Select motor and gearbox separately and assemble
Method 2: Select a pre-engineered gearmotor (geared stepper motor nema 8, geared nema 11 stepper motor,geared stepper motor nema 14) .
While both methods 1 and 2 are effective means of finding the most compatible gearmotor, Method 2 reduces design time and project risk for the designer. When selecting a pre-engineered solution, the manufacturer has done much of the heavy lifting to ensure that the motor and gearbox combination will work properly together.
NEMA Size is "National Electrical Manufacturers Association
Samstag, 11. August 2018
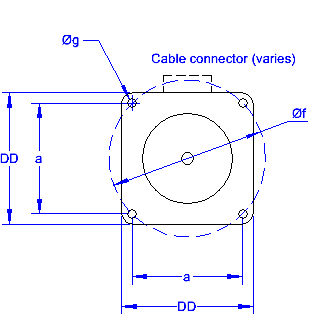
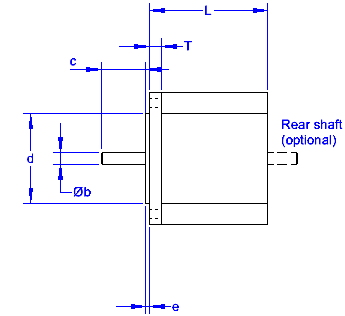
NEMA is "National Electrical Manufacturers Association" and their standard for motor mounts is commonly used in the industry to ensure that replacement parts will fit and be readily available, and that motors from different mfgs will be interchangeable. The NEMA number is related to the diameter of the motor times 10. So a NEMA 23 motor is 2.3 inches around or down the side.
| Dimension in Inches (mm) | NEMA Motor Mounting Dimensions | ||||||
| NEMA 8 | NEMA 11 | NEMA 14 | NEMA 17 | NEMA 23 | NEMA 34 | NEMA 42 | |
| Motor Size (DD) | ~0.8 | ~1.1 | ~1.4 | ~1.7 | ~2.3 | ~3.4 | ~4.2 |
| a: Bolt Hole Distance (square) | 0.630 (16) | 0.905 (23) | 1.024 (26) | 1.220 (31) | 1.854 (47.14) | 2.744 (69.7) | 3.500 (88.9) |
| b: Motor Shaft Diameter | 0.157 (4) | 0.197 (5) | 0.197 (5) | 0.197 (5) | 0.250 (6.35) | 0.375 (9.5) | 0.625 (16) |
| c: Motor Shaft Length (max) | 0.945 | 0.810 | 1.250 | 1.380 | |||
| d: Pilot Diameter | 0.590 (15) | 0.866 (22) | 0.866 (22) | 0.866 (22) | 1.500 (38.1) | 2.875 (73) | 2.186 |
| e: Pilot Depth (max) | 0.059 (1.5) | 0.079 (2) | 0.079 (2) | 0.079 (2) | 0.062 (1.6) | 0.062 (1.6) | 0.062 (1.6) |
| f: Bolt Hole Circle Diameter | 1.725 | 2.625 | 3.875 | 4.950 | |||
| g: Bolt Hole Size | 0.118 (3) | 0.157 (4) | 0.157 (4) | 4-40 UNC | 0.195 (5) | 0.218 (5.5) | 0.281 |
| Thanks to Neil (PICDude) for these excellent pictures! |
he primary NEMA number specifies the position and size of the mounting face as shown in the table above. The full NEMA standard also describes other features of the motor. The full NEMA description of a stepper motor for sale is written as:
NEMA DDMMLLL-CCCIVVVSSSW, where:
- DD is diameter (inches x 10). For square stepper motors, the length of a side is used instead of the diameter.
- MM is mount type code (inches x 10), include none, one or both of these letter codes
- "C" if there are holes tapped in the face of the motor
- "D" If there is a flange on the back end of the motor with slots missed for bolts to pass through
- LLL is length (inches x 10),
the "-" at this point separates mounting info from electric characteristics. - CCC is phase current (amps x 10),
- I is insulation class and defines the maximum allowable operating temperature
- Class A is 221'F
- Class B is 266'F
- Class F is 311'F
- Class H is 356'F
- VVV is phase voltage (rating x 10),
- SSS steps per revolution,
- W is a winding code.
- A is two wires,
- B is 3 wires,
- C is 4 wires,
- D is 5 wires,
- E is 6 wires,
- F is 8 wires
For example: a 3.4" diameter stepper motor with a flange that is 1.6 inches long, has a phase current of 1.2 Amps, class B insulation, 5.3 phase voltage, 200 steps per revolution, and 8 wires is: NEMA 34 motor D016-012B053200F
